The term ‘Aquaponics’ is made of two words – ‘aquaculture’ and ‘hydroponics’, which means it combines cultivation of fish in the aquarium and various plants in water.
The essence of such a combination is the water circulation from the aquarium to ‘grow bed’ and its purification through the hydroponics system while plants get necessary nutrients. Since every system provides what the other system lacks, you will get both clear aquarium and organic food in your home. Let’s see what it is actually about.
Definition of Aquaponics
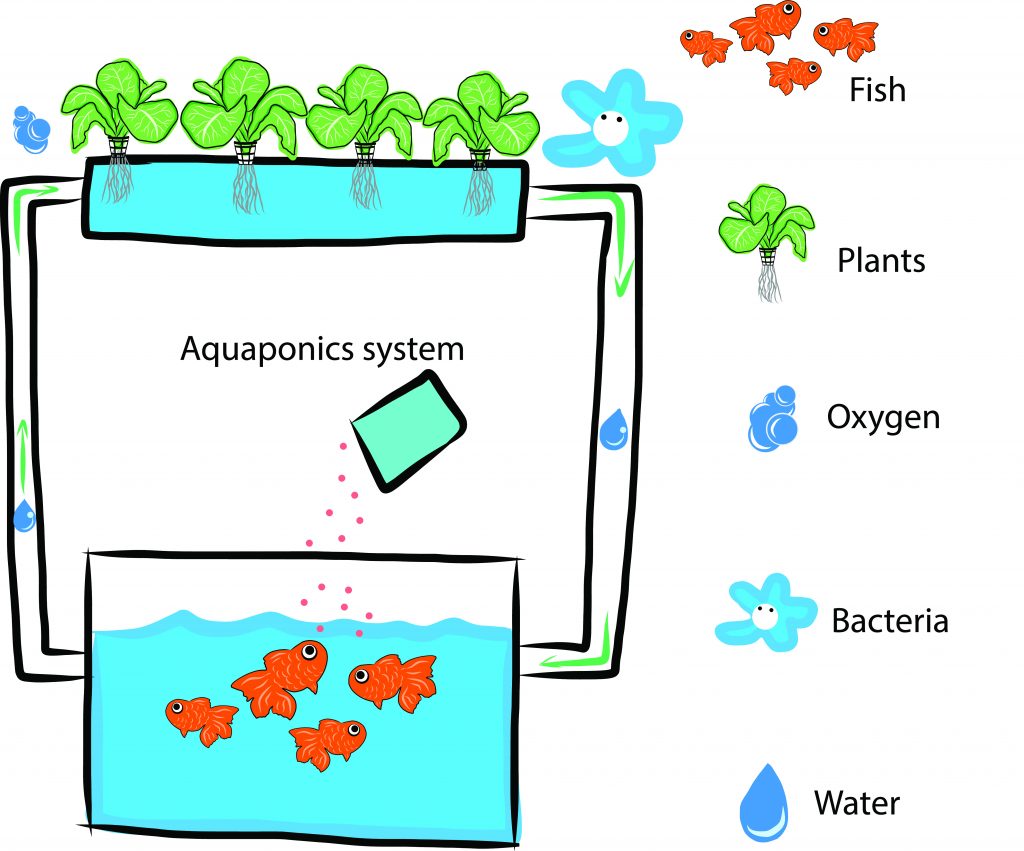
The definition of ‘Aquaponics’ says that it is a system of aquaculture which implies feeding plants that you grow hydroponically by using the farmed fish’s waste products. In return, those plants purify the water in your aquarium. The results are an inexpensive, eco-friendly aquarium and production of food in cramped space at the same time.
Aquaponics system has become a popular method of cultivating plants in urban areas where there is no possibility of growing classical gardens. Generally, anyone can create and use this practical system and get higher food yields in their own home.
The benefits of this kind of vegetable cultivation are numerous:
- Anyone can make this system
- There is a possibility to design and install home aquarium aquaponics in every apartment, no matter how small it is
- It is a clean, closed system for growing both fish and plants
- It saves water thanks to its re-using
- It is a soil-free system and doesn’t exhaust soil nutrients
- It doesn’t use pesticides
- It is an eco-friendly system and doesn’t pollute the environment
- There is no waste
- There is no fear of deforestation in order to provide new arable land
- It requires very little work
It is a truth that professional aquaponic systems are expensive, but you need just a little creativity, enthusiasm, and a small pump to make your own setup for home use.
How to DIY the Aquaponics System
When you start thinking about installing this system in your home, you should consider a few critical issues:
1. Environmental factors

Before installing the system, consider possible problems and ways to overcome them:
- Humidity – Since aquaponics is a system with constant water flow through its two parts, you need to count on the natural evaporation and consequential increased moisture in your space. Also, you need to heat the water in your aquarium. When the air in the apartment is cooler, or there is poor air circulation, the temperature difference will cause extra humidity.
- Water spillage – The fact is that aquaponics can leak no matter how careful you will be with water. Therefore, the room where you want to create this system should be waterproof and without stuff that water can damage. Be careful with electric appliances you use near the aquarium. Be prepared in advance for possible spillages.
- Lighting – Even though the HIDs system (high-intensity discharge system) spends a lot of energy, it proved to be the best for use in the apartment.
Your goal is to live in harmony with ecological principles, but be prepared that not one such system is perfect. For example, if you decide to install aquaponics, you have to count on high electricity bills.
If you just want a small home Aquaponics system, here are our picks of aquaponics kit for you.
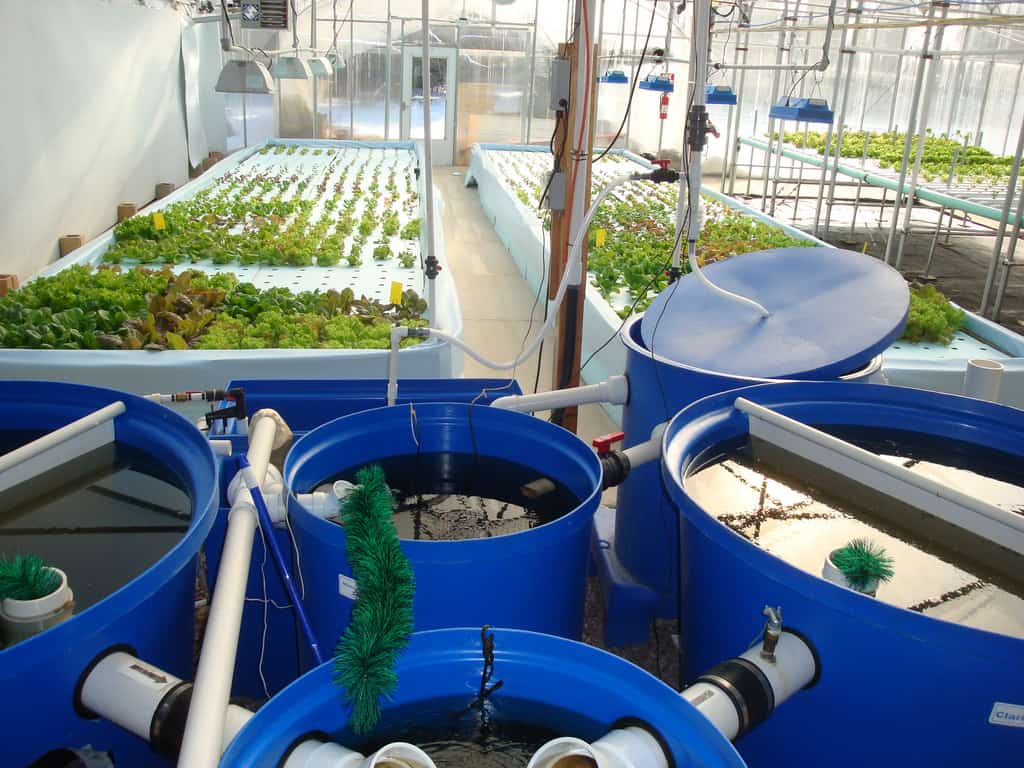
2. Components of the aquaponics system

To get an efficient system, you need to buy some essential components:
Aquaponics fish tank (aquarium)

If you are a novice and want to grow your plants in a small system, you can use a traditional aquarium (made of glass or plastic). It is also possible making this system from tanks, tubs, or barrels.
A well-tuned professional aquaponics system implies one pound (0.45 kg) of fish per gallon (3.8 l) of water. If you are just starting to do this kind of planting, it is better to calculate ten gallons (10 l) of water for one fish.
Judging by my experience and talking with do-it-yourselfers, most of them begin with a 55-gallon (208 l) barrel. How this process will further develop depends only on you, your will and skills.
Flood trays (grow trays)
It is a foundation for your future ‘garden’. Its size directly depends on the size of your aquarium. That means that you can cultivate as many plants as you have fish in the aquarium. In the beginning, you can count on one plant per fish.
Grow bed for your plants
It is actually a big water-resistant container where you will grow your plants. You can buy one or make it by yourself. The simplest grow bed is a six to ten inches (15-25.5 cm) deep wooden box lined with the edge of your aquarium and filled with a chemically soil-free medium.
Grow media

Its purpose is to provide support, drainage, and aeration of your aquaponic system. You can use perlite, coco coir, fine gravel, or a mixture of all three in equal proportions. Also, many people prefer stones and clay pebbles because they are decorative.
Support
You can use anything that is large enough to support your system, including concrete blocks, shelves, or a table. The only thing you should secure is to make a structure sturdy enough to support the grow bed.
Pipes (or siphons)
You need them for returning filtered water from the grow bed back into the fish tank. The most reliable systems are:
- Ebb and Flow
- Bell siphons
- Piping drains
Water pumps

They transport water from your fish tank to the grow bed. That way plants won’t need for fresh water because they will use aquarium liquid with the fish’s waste products full of nutrients.
Also, it will transport filtered water from the grow bed to the fish tank which will allow this independent system to form a closed circle. For an entirely self-sufficient system, you need to install a solar-powered pump. You will need:
- Water pumps that will ensure that water continually flows throughout your system
- Air pumps that will provide oxygen to your aquarium
Timers
Some aquaponics systems don’t need timers, but you should purchase one if you want bigger, more complicated, and advanced design. Whether you use a basic timer or highly programmable one will depend on you and what type of system you want to install.
Aerator
This critical piece of hardware will provide an adequate amount of oxygen for your fish.
Best Fish for Your Aquaponics
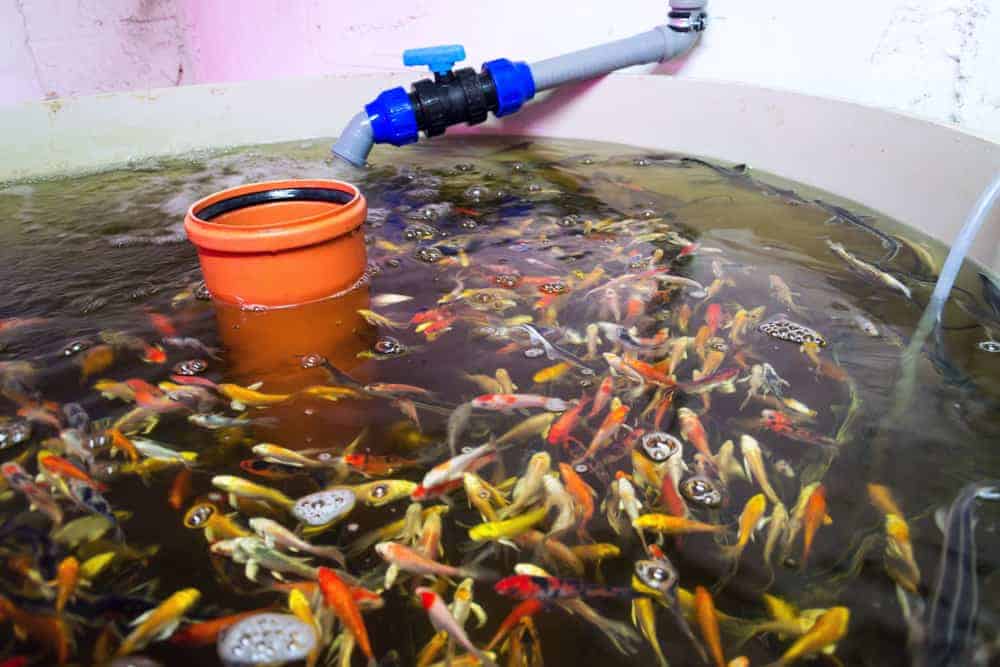

Without adequate fish, there are no aquaponics systems since they provide necessary nutrients for your herbs. Therefore, you need to carefully select the best varieties of fish for your aquarium depending on:
- The type of aquaponics system
- Water temperature
- The region you live
- The kind of plants you want to grow
If your ambition is a small-scale indoor aquaponics to produce some veggies, every fish from your aquarium is good enough. After all, you don’t want to eat those fish; you just need their stools. Pick out traditionally desirable angelfish, goldfish, Koi fish, and guppies, and enjoy your lovely design.
When you decide that aquaponics is more than a joy for you, choose species depending on your environment. For warm climates, where the water temperatures are from 80 and 90 F (26.7-32 C), pick out Channel Catfish, Barramundi, Tilapia, or Jade Perch. Keep in mind that they can’t survive temperatures lower than 72 F (22 C).
If you can’t provide water warm enough for these exotic creatures or you live in the colder region, you should make a different choice and buy cold water fish. For places where the water temperature is never above 70 F (21 C), most suitable species are white bass, trout, or carp.
The most suitable fish for the aquaponics system are:
- Tilapia – It is the most desirable tropical species for small scale systems due to their excellent growth rate, high tolerance to imperfect water conditions, and a harvestable size of one pound (0.45 kg) in six months.
- Catfish – They tolerate cold climate, but keep in mind that you need to provide warmer water if you want young fish to develop properly and be healthy.
- Yellow perch – It is a pretty common species for aquaponics systems because they can put on growth at lower water temperatures.
Best Plants for Your Aquaponics
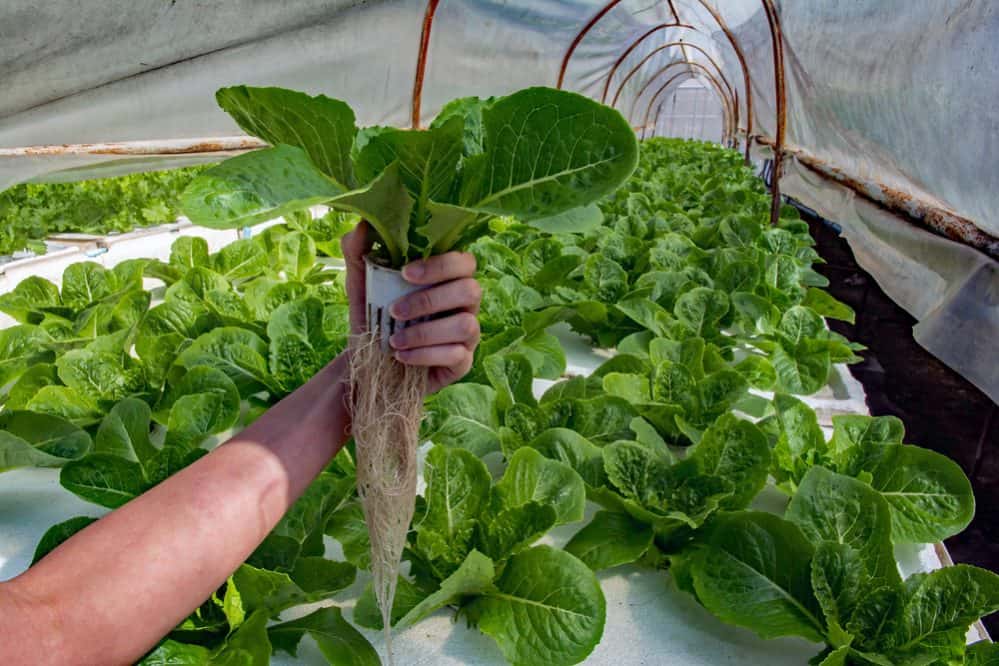

Your aquaponics garden can support many herbs (chives, basil, mint, dill, or parsley), veggies (kale, cabbage, chard, lettuce, arugula, or spinach), fruit (strawberries, raspberries, or blueberries), and houseplants (philodendron, anthodium, dieffenbachia, or dracaena). Avoid planting potatoes, carrots, and any other veggies that grow underground.
If you choose to plant tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers, or eggplants, you should be aware that these vegetables are demanding of nutrients and need higher temperatures. On the contrary, lettuce and cabbage prefer cooler conditions. Shortly speaking, you will get the best results if you pick out plants that suit the climate in your region.
The best solution is to sow seeds in jiffy cubes (grow cubes), but you can also transplant seedlings if you prefer that way. Just be sure to wash all of the soil from the roots and remove pest insects from foliage.
Don’t forget to add some aquatic plants in your fish tank to provide as much as the natural habitat for your lovely fish.
The Importance of Nitrification Cycle
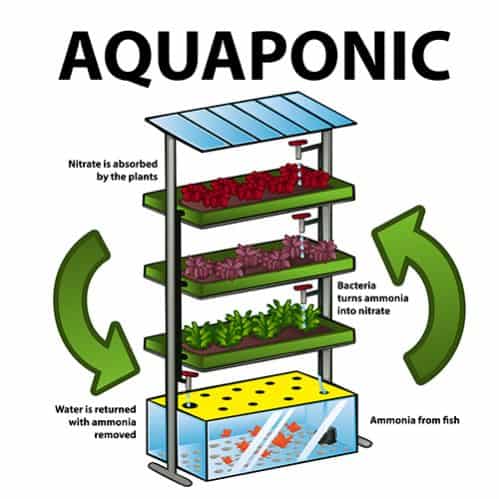
Usually, the biggest problem with a fish tank is ammonia. This element accumulates in the classical aquarium and represents a significant challenge for fish health and wellbeing.
The advantage of your aquaponics is that there are many nitrifying bacteria in the system (from plants and fish bodies). After the fish extract ammonia into the water, these microorganisms convert excess of it (in the presence of oxygen) to harmless nitrates which plants use for their growth and flourishing.
That simple process makes aquaponics system the efficient way of regulating the nitrogen levels, balancing the water pH levels, and reducing the ammonia in water to the amount that is safe for your fish.
You only have to check the level of ammonia and pH levels once a week and the amount of nitrates once a month. Anyone who has an aquarium knows what a relief it can be.
Aquaponics System Maintenance
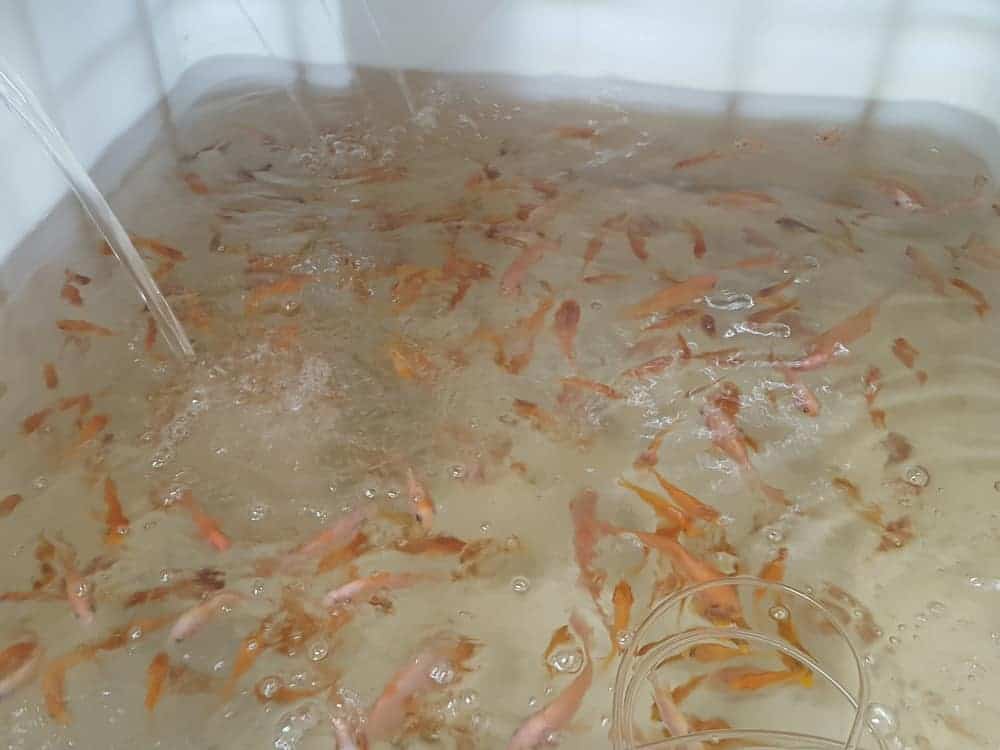

As far as your fish are concerned, the only thing you need to do is to feed them daily. Always keep in mind that the best portion is the one that your fish can eat in five minutes.
Basically, it is better offering fish frequent small feedings than giving them a large amount of food once a day. Give your tropical fish a dry flake fish food but occasionally add some bloodworms and brine shrimp to keep them healthy.
Additionally, check the level of water and add some when needed. Once a month, you should replace a 10 to 15% of the aquarium water with a fresh one.
The Benefits of Aquaponics over Standard Soil
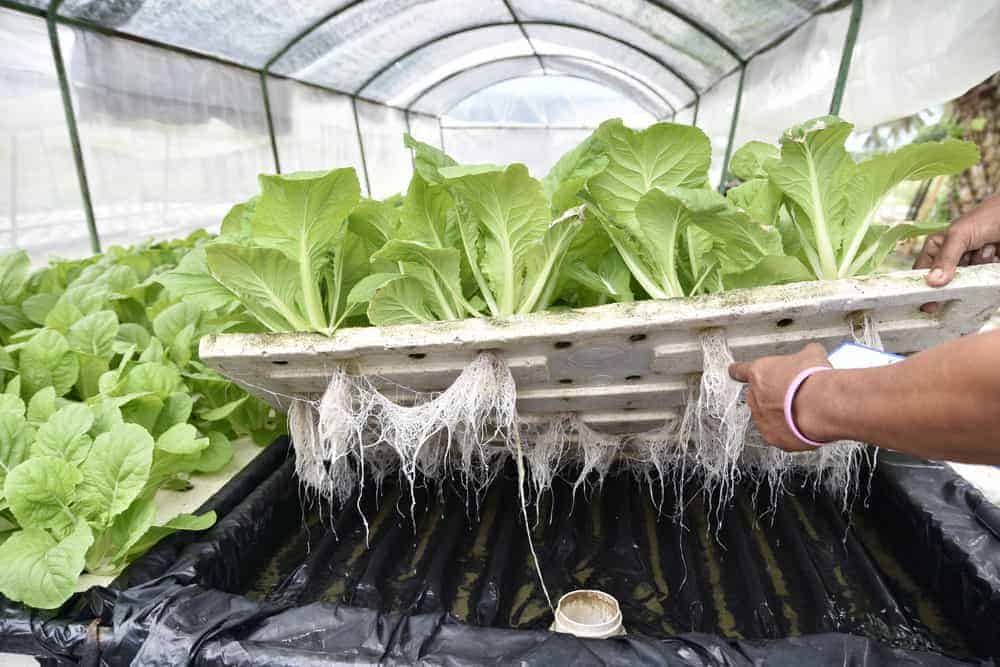

Aquaponics systems are probably our future because they offer many advantages. I will give you the essential ones:
- Organic food – Since it is an organic system, the food we get is going to be also organic. There are no pesticides, insecticides, and any horrible synthetic chemicals we usually need to use in the traditional garden.
- Water saving – Thanks to re-circulating, this system uses one-tenth of the water needed for a traditional garden.
- Natural fertilizer – You don’t need any fertilizer because all nutrients from fish waste feed your plants automatically. Once the system is balanced, your plants will receive all they need 24/7.
- Waste management – It is an efficient way to get rid of fish waste which is basically a pollutant.
- Weeds – This system is entirely weeds-free.
Disadvantages of Aquaponics
Most articles you can find about aquaponics systems usually praise them as best-of-the-best, but you shouldn’t forget that no one system is ideal. Actually, aquaponics can be a very challenging venture, especially for beginners. It requires a lot of patience and incredible persistence.
- Cost – Even though a smaller aquarium won’t require much investment, bigger systems for serious growers cost money. All these fish, plants, and devices can be pretty expensive.
- Fish food – Since most manufacturers use wild seafood for making fish food, it is not eco-friendly and can be pretty expensive.
- Stabilization of the system – System stabilization can be a significant challenge, especially for beginners. This process takes time, and if you use aquaponics for serious vegetable’s production, the question of profitability arises as well.
Summary
Although this way of growing plants has several significant disadvantages, all the odds are that aquaponics is our future. That is an organic and healthy way for you to produce veggies and fish meat for you and your family without undesirable GMOs, chemicals, and fertilizers, as well as antibiotics overloads.
Along with all the advantages of the aquaponics systems and a real opportunity to find a way to overcome its negative sides, I truly believe that this system will become a part of our everyday lives very soon.
Let’s save our polluted planet together!

Informative & a great insight
Interesting
I’m going to try it
could you send all the thing
Beautifully written and presented guide – thanks for sharing. I absolutely agree with the final sentiment – it’s our responsibility to do something about the current state of affairs and strive for a better, cleaner, more green Earth. Keep up the great work!